Funding
The estimated cost of construction of the I-78 Lenhartsville Bridge Replacement Project is between $40 and $50 million.
PennDOT Pathways is a program to identify and implement alternative funding solutions for Pennsylvania's transportation system. As Pennsylvania's mobility needs have grown, the amount of funding required to support our transportation system has continued to increase. Much of our current funding comes from gas taxes and driver and vehicle fees. While this model worked well in the past, circumstances today have made it unsustainable. With PennDOT Pathways, we're looking for reliable, future-focused funding solutions that will meet our growing needs while serving our communities and all Pennsylvanians for generations to come.
PennDOT currently faces an $8.1 billion gap in highway and bridge funding. This means we aren't generating enough funds to properly maintain, restore and expand our transportation system. PennDOT is taking action to find reliable sources of funding through the PennDOT Pathways program.
For more information about PennDOT Pathways, visit www.penndot.gov/funding.
One of the funding solutions identified in the Planning and Environmental Linkages (PEL) Study was the implementation of bridge tolls on major bridge projects across the state. The I-78 Lenhartsville Bridge Replacement Project is one of several projects being evaluated as a candidate for bridge tolling as a part of the PennDOT Pathways Major Bridge P3 Initiative. You can learn more about the program and initiative at the link above.
A bridge toll is a fee that drivers pay when using a specific bridge, often by using a service like E-ZPass. The funds received from the bridge toll would go back to the I-78 Lenhartsville Bridge to pay for its construction, maintenance and operation.
To implement the toll with All-Electronic Tolling (such as E-ZPass or toll-by-plate), a tolling facility (gantry, building and utilities) will be constructed approximately 1,700 feet east of the new bridge and will require the installation of small driveway/parking area along the eastbound shoulder for maintenance pull-out and access. The tolling facility will not require drivers to stop to pay a toll when using the bridge but will record vehicles as they pass under the gantry sensor. A map of the toll gantry location is below.
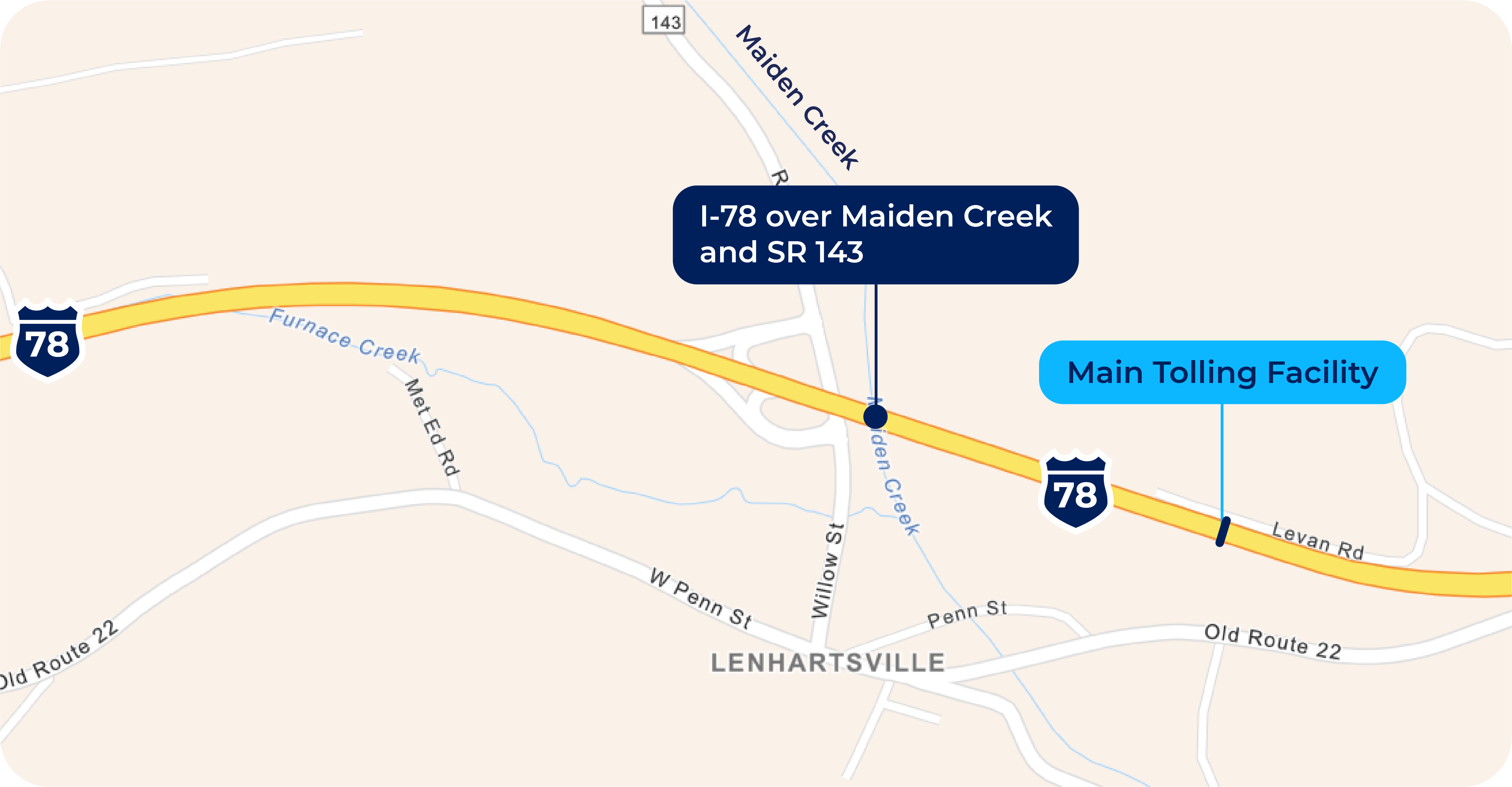
In addition, signs will be placed about 1 mile prior to the tolling facility in each direction to inform drivers about the toll bridge, as well as at the nearest interchanges and their respective local roadway network (i.e., Exit 35 to SR 143/Lenhartsville and Exit 40 to SR 737/Krumsville/Kutztown).
PennDOT has established that tolls on the candidate bridges, including the I-78 Lenhartsville Bridge, would be in the range of $1-$2 for cars using E-ZPass and higher for toll-by-plate and for medium or heavy trucks. Exact tolling amounts will be determined once design plans are finalized so the toll would generate enough revenue for the bridge's replacement, operations, and maintenance for a period of approximately 30 years. At the end of the 30-year term for the Public-Private Partnership (P3), the tolling facility would be removed.
Qualifying emergency vehicles would be permitted to use Pathways' bridges at no cost, following the Pennsylvania Turnpike Policy (PDF).
It is expected that toll collection on the bridge would begin between 2023 and 2025.